Abstract
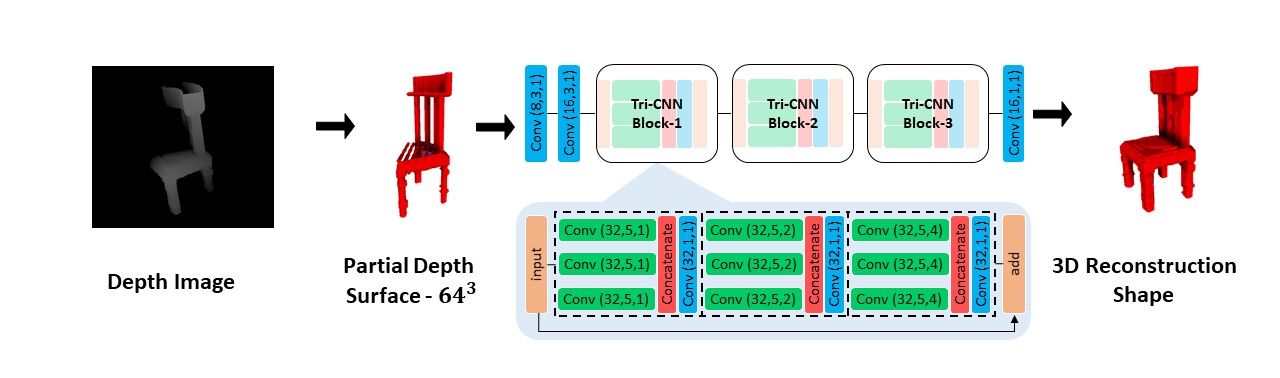
In this study, the authors propose a novel three-dimensional (3D) convolutional neural network for shape reconstruction via a trilateral convolutional neural network (Tri-CNN) from a single depth view. The proposed approach produces a 3D voxel representation of an object, derived from a partial object surface in a single depth image. The proposed Tri-CNN combines three dilated convolutions in 3D to expand the convolutional receptive field more efficiently to learn shape reconstructions. To evaluate the proposed Tri-CNN in terms of reconstruction performance, the publicly available ShapeNet and Big Data for Grasp Planning data sets are utilised. The reconstruction performance was evaluated against four conventional deep learning approaches: namely, fully connected convolutional neural network, baseline CNN, autoencoder CNN, and a generative adversarial reconstruction network. The proposed experimental results show that Tri-CNN produces superior reconstruction results in terms of intersection over union values and Brier scores with significantly less number of model parameters and memory.